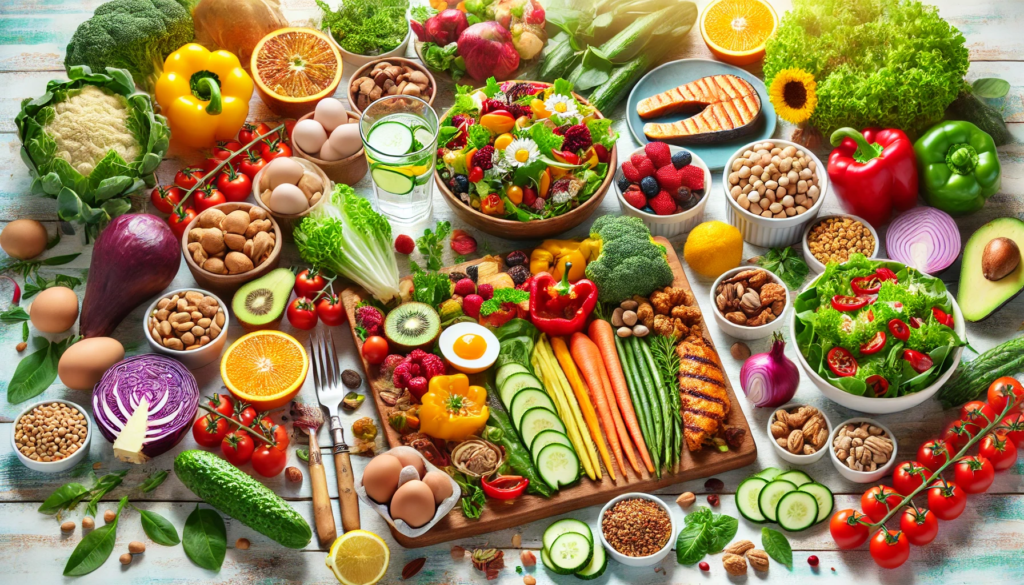
The flexitarian diet is a flexible approach to eating that primarily focuses on plant-based foods while allowing for moderate consumption of animal products. The term “flexitarian” combines “flexible” and “vegetarian,” highlighting the diet’s adaptable nature. This guide explores the principles of the flexitarian diet, its benefits, and how to incorporate it into your lifestyle.
What is the Flexitarian Diet?
The flexitarian diet encourages eating mostly plant-based foods, such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains, while permitting occasional inclusion of meat, poultry, fish, and other animal products. Unlike strict vegetarian or vegan diets, the flexitarian approach is less restrictive, offering more flexibility and making it easier to adopt and maintain.
Key Principles
- Emphasize Plant-Based Foods: Focus on incorporating a variety of plant-based foods that are rich in nutrients, fiber, and antioxidants.
- Include Animal Products in Moderation: While plant-based foods are the foundation, small amounts of animal products can be included, depending on personal preference and dietary needs.
- Limit Processed Foods: Prioritize whole, minimally processed foods over highly processed options.
- Choose Nutrient-Dense Foods: Opt for nutrient-dense choices that provide essential vitamins, minerals, and other beneficial compounds.
- Be Flexible: The diet allows for flexibility, making it easier to adjust based on individual dietary preferences and lifestyle changes.
Benefits of the Flexitarian Diet
1. Nutritional Balance
The flexitarian diet offers a balanced intake of essential nutrients by combining the benefits of plant-based foods with the nutritional value of animal products. This balance helps meet protein needs, essential fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals that may be harder to obtain on a strict vegetarian or vegan diet.
2. Heart Health
A diet rich in plant-based foods and low in saturated fats can support heart health. Consuming more fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains can help lower cholesterol levels, reduce blood pressure, and decrease the risk of heart disease.
3. Weight Management
The emphasis on plant-based foods, which are generally lower in calories and higher in fiber, can aid in weight management. The diet promotes satiety and helps prevent overeating, making it easier to maintain a healthy weight.
4. Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases
Plant-based diets have been associated with a reduced risk of chronic diseases, such as type 2 diabetes, certain cancers, and metabolic syndrome. The flexitarian diet, with its focus on nutrient-dense foods, can contribute to overall disease prevention.
5. Environmental Benefits
Reducing meat consumption can lower the environmental impact associated with livestock production, including greenhouse gas emissions, land use, and water consumption. The flexitarian diet supports sustainable eating practices by encouraging more plant-based meals.
6. Flexibility and Inclusivity
The diet’s flexible nature makes it accessible and inclusive, accommodating various dietary preferences and cultural practices. It allows for occasional indulgences and adjustments, making it more sustainable in the long term.
How to Follow a Flexitarian Diet
1. Plan Plant-Based Meals
Start by planning meals that focus on plant-based ingredients. Incorporate a variety of vegetables, fruits, legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains into your daily diet.
2. Include Animal Products Sparingly
Incorporate animal products in moderation, such as a few times a week. Choose lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products. Consider sourcing sustainably and ethically produced animal products.
3. Experiment with Plant-Based Proteins
Explore plant-based protein sources, such as beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, and quinoa. These options provide high-quality protein and can be used in a variety of dishes.
4. Prioritize Whole Foods
Opt for whole, minimally processed foods to maximize nutrient intake. Avoid highly processed foods that are high in added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium.
5. Be Mindful of Portions
Pay attention to portion sizes, especially when including animal products. A balanced plate should prioritize plant-based foods, with smaller portions of animal products.
6. Stay Hydrated
Drink plenty of water throughout the day and include hydrating foods, such as fruits and vegetables. Limit sugary beverages and alcohol.
Conclusion
The flexitarian diet offers a balanced and flexible approach to eating, combining the benefits of plant-based foods with the occasional inclusion of animal products. It promotes a diverse and nutrient-rich diet that supports overall health, weight management, and environmental sustainability. Whether you’re looking to reduce meat consumption, explore plant-based options, or simply adopt a more balanced diet, the flexitarian approach can be a practical and enjoyable way to achieve your dietary goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often can I eat meat on a flexitarian diet?
The flexitarian diet does not have strict rules about the frequency of meat consumption. It encourages reducing meat intake and prioritizing plant-based foods, but you can include animal products a few times a week or less, depending on your preferences and health goals.
Can I get enough protein on a flexitarian diet?
Yes, you can get enough protein on a flexitarian diet by including a variety of plant-based protein sources, such as beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, nuts, seeds, and whole grains, along with moderate amounts of animal products.
Is the flexitarian diet suitable for everyone?
The flexitarian diet is generally suitable for most people, as it is flexible and can be tailored to individual needs and preferences. However, those with specific dietary restrictions or medical conditions should consult with a healthcare professional before making significant dietary changes.
What are some easy plant-based meal ideas?
Some easy plant-based meal ideas include vegetable stir-fries with tofu, lentil soups, chickpea salads, grain bowls with roasted vegetables, and pasta dishes with marinara sauce and vegetables.
Can I follow a flexitarian diet if I’m lactose intolerant?
Yes, you can follow a flexitarian diet if you’re lactose intolerant by choosing lactose-free or plant-based dairy alternatives, such as almond milk, soy yogurt, and vegan cheese.
How can I make sure I’m getting enough nutrients on a flexitarian diet?
To ensure you’re getting enough nutrients, focus on a diverse and balanced diet that includes a variety of plant-based foods and occasional animal products. Consider taking a multivitamin or specific supplements if needed, and consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.